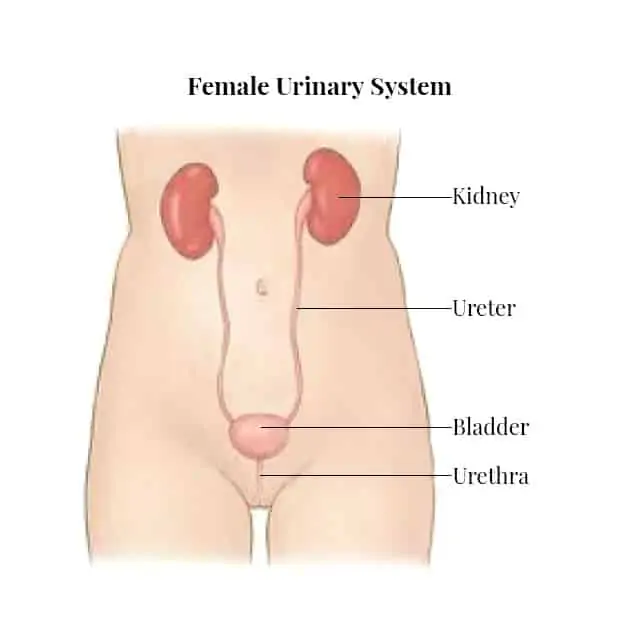
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra. Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI as compared to men. Approximately 40% of women develop a urinary tract infection (UTI) at some point in their life. The condition is uncommon in boys and young men.

Symptoms of UTI
Urinary tract infections do not always have signs and symptoms, however when they appear, they may include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Urine that appears pinkish — a sign of blood in the urine
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain (in women) — especially in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone
 Menopause. After menopause, a decline in circulating estrogen causes changes in the urinary tract and reduces its ability to resist bacteria invasion.
Menopause. After menopause, a decline in circulating estrogen causes changes in the urinary tract and reduces its ability to resist bacteria invasion.
In males, UTI can develop due to urinary tract abnormalities, blockages in the urinary tract due to kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, which traps urine in the bladder.
 100vw, 1280px” data-lazy-src=”https://www.rafflesmedicalgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/health-resource-subscribe.webp” /></a></figure><h3>Diagnosing UTI</h3><p>Your doctor will use the following <strong>tests</strong> to diagnose a urinary tract infection:</p><ul><li><strong><span class=) Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
Treatment for UTI
Mild cases may disappear spontaneously without treatment. However, because of the risk of the infection spreading to the kidneys, antibiotics are usually recommended. Prompt treatment is recommended for the elderly due to the high mortality rate in this group.
Preventing UTI
- As the source of the bacteria often comes from one’s own bowel, wipe yourself from the front to back to avoid faecal contamination of the urinary tract (especially during an episode of diarrhoea) after going to the toilet.
- Avoid potentially irritating vaginal deodorants and bubble baths and maintain a high standard of personal hygiene. This involves washing the genital area with water while showering and especially after intercourse. Voiding soon after intercourse is also encouraged.
- Any vaginal/ lower genital tract infection should be treated. Otherwise, the infection may spread to the urinary tract.
- For healthy individuals, it is recommended to drink a minimum fluid intake of 2 litres a day (more if exercising strenuously or on hot days).
- Regular and complete bladder emptying is advisable to prevent the accumulation of infected urine in the bladder.